Endocrine Conditions
Conditions
Allied Support
Heart Disease
Knowledge is Power.
True/False - Quiz: Do You Understand Heart Disease?
Information - Heart Disease
 Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men and women in North America. Heart disease refers to many conditions that affect the heart, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias), congenital heart defects and more.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men and women in North America. Heart disease refers to many conditions that affect the heart, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias), congenital heart defects and more.
Common Types of Heart Disease
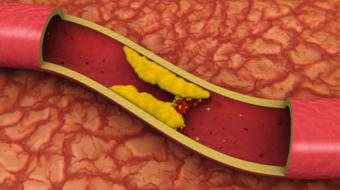
Coronary artery disease: As plaque builds up it narrows your coronary arteries, decreasing blood flow to your heart. This decreased blood flow can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations and sweating. A complete blockage can lead to a heart attack.
Congenital heart disease: Congestive heart failure is a chronic heart condition that occurs when your heart muscle is ineffective at pumping blood. Certain heart conditions such as high blood pressure or coronary artery disease can lead to congestive heart failure. While the term "heart failure" is often used used, congestive heart failure is the stage in which fluid builds up around the heart, causing it to pump inefficiently.
Arrhythmia: Also known as atrial fibrillation, it can increase your risk of heart failure, stroke, blood clots and other heart conditions. A normal heart contracts and relaxes to a regular beat, but if you have atrial fibrillation, the atria (upper chambers) beat out of sync with the ventricles (lower chambers). This can cause blood to pool in your atria, causing blood clots that travel to your brain and cause a stroke.
Heart Disease Symptoms & Treatment
 Heart disease symptoms depend on the type of heart disease you have. However, there are some common cardiovascular disease symptoms that many people experience including:
Heart disease symptoms depend on the type of heart disease you have. However, there are some common cardiovascular disease symptoms that many people experience including:
• Pain, aching or discomfort in the chest and arm (can spread to other parts of the body)
• Nausea or vomiting
• Dizziness
• Sweating
• Restlessness
If you or someone around you is experiencing heart attack symptoms, call 911 immediately. Treatment for heart disease depends on your condition, and may include:
• Antiplatelet drugs such as aspirin to keep blood clots from forming
• Anticoagulants (blood thinners) to keep blood from clotting or prevent existing clots from getting bigger
• Beta blockers to slow the heart and reduce its workload
• Blood cholesterol-lowering agents to decrease LDL cholesterol levels in the blood
• Calcium channel blockers to relax blood vessels
• Nitrates (nitroglycerin) to stop chest pain and relax blood vessels
• Thrombolytic agents (clot busting drugs) to treat a heart attack
In many cases, heart disease can be prevented by controlling risk factors. Risk factors for heart disease include obesity, high blood pressure, smoking, high cholesterol and diabetes. The best place to start is with your physician – he or she can help you get on the right track with diet, exercise and lifestyle modifications.
Talk to your cardiologist if you'd like more information on heart disease.
Visit HealthChoicesFirst.com for more videos and resources on heart health.
Print this Action Plan and check off items that you want to discuss with your healthcare provider
-
Coronary artery disease occurs when plaque builds up and narrows your coronary arteries. This decreases blood flow to your heart, which can can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations and sweating. A complete blockage can lead to a heart attack.
-
Congestive heart failure is a chronic heart condition that occurs when your heart muscle is ineffective at pumping blood.
-
Arrhythmia (also known as atrial fibrillation) can increase your risk of heart failure, stroke, blood clots and other heart conditions.
-
Treatment for heart disease depends on your condition, and may include antiplatelet drugs, anticoagulants, beta blockers, nitrates, calcium channel blockers and others.
-
In many cases, heart disease can be prevented by controlling risk factors. Risk factors for heart disease include obesity, high blood pressure, smoking, high cholesterol and diabetes.

